*Hiroshige's Goto Weekly overseas news*
Current PSP only efficiency of 2/3 being able to show the reason which is not
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- As for operational frequency it was not 333MHz and was 222MHz
The PSP tip/chip was operational to tell the truth with only the clock of 2/3 of the specifications. Current PSP still being able to show full performance means not to be. In addition, the OS kernel of PSP among the main memories of 32MB, had possessed the 8MB thing area. This is large to exceptional case as a OS kernel area of the game machine.
The motherboard of PSP
In the middle of March was held "GDC (Game Developers Conference)" with, the side which is not excessively known so far generally concerning PSP, made clear. SCEA (Sony Computer Entertainment America), the session which is entitled "PSP Advanced Software Overview" was done with GDC. Among those, Mark DeLoura of SCEA (Manager of Developer Relations), update and software layer of the PSP hardware specifications and the entire image of the tool were explained.
In former official announcement, as for operational frequency of the CPU core of PSP with コンフィギ…ラブル, it was the expectation which operates at most 333MHz. But, with GDC, as for the CPU core of PSP, as for present condition when it is restricted in 222MHz, it was explained. It means to be held down to the clock of 2/3 of the specifications exactly. In addition, also bus speed, 166MHz at the time of specifications announcement of the year before last (reverse operation) from is backing up to maximum 111MHz from zone.
"As for CPU is the range to 333MHz, but under present conditions it is locked to 222MHz. Because the bus is typically the half of CPU (the clock), it has become 111MHz. When CPU is pulled up to 333MHz, when deciding, also the bus is pulled up probably will be to 166MHz, "that DeLoura explains.
The down grade to 222MHz has suggested that in provisional specification, there is a possibility of pulling up in the future to 333MHz. In the future, moving to 65nm process and the production process after the that, perhaps at the stage where electric power consumption goes down, to 333MHz it makes improvement possible.
SCEA did not explain the reason where it is restricted to 222MHz finely. But, as recognized even from the fact that this specification modification is explained with the corner of economical electric power, as for low frequency conversion for electrical retrenchment as for being it is clear. PSP, under the present conditions of 222MHz, to use comfortably with the lithium ion battery of 1,800mAh as an operation and a game machine of 4 - 6 hours, is the last line. Because of that, above this increasing CPU frequency, increasing electric power consumption, it is presumed that it was not possible to shave battery drive time. It seems that as for actual solution with semiconductor technology of present condition, is not 333MHz and is 222MHz.
Summary of CPU core. Frequency has become 222MHz with default The graphic engine under present conditions operates with 111MHz
- The electric power consumption decrease of PSP whose hardship is many
Those where it is distinct from the frequency lock of PSP, are that also SCEI and have suffered hardship in electric power consumption decrease. Especially, in case of PSP becoming problem TDP (Thermal Design Power: It is average electric power consumption not only thermal design electric power consumption). As for average electric power consumption, because leak (a leak) electric current echoes largely, with the process which the present time refines it is very difficult to lower. With improvement such as process technology and circuit design, how much can reduce leak electric power, it is one of the future technical hurdles of PSP.
Though, when you look at the whole PSP, the fact that electric power is eaten on the other hand seems like the device other than main chip set. In the explanation with GDC, seeking and the wireless LAN of UMD drive (Wi-Fi), high brightness setting and the like of liquid crystal display, when it is the operation which consumes electric power very it was explained. Conversely, as for electricity consumption being little, you say that it is the media engine, the bus and the memory stick.
As for the media engine which includes AVC decoding because rather to hard wired it is converted, electricity consumption is little. In 2004 August HotChips conference as for average electric power consumption at the time of AVC decoding below 500mW it was explained. As for the bus, it is seen that is, because economical electrical conversion is possible by the fact that it TURNS OFF briskly.
PSP in the future economical electrical conversion of UMD drive and wireless LAN module etc. becomes necessary. In order with GDC to hold down the access to UMD, it called. In addition, economical electrical conversion of wireless LAN module, as wireless LAN corresponding title increases, probably becomes the important element.
The 222MHz lock is produces effect to also software development. For example, when at the point in time when it reaches the point where it can utilize the frequency to 333MHz, the software where the load which uses the full CPU clock is high was made, there is a possibility the case where compatibility of the current type of 222MHz becomes problem coming out. But, when you see in positive, PSP specifications means to be the margin where still it improves performance.
The largest obstacle economical electric power of PSP. As for CPU under present conditions lock to 222MHz When developing the battery emulator tool in order to optimize electric power consumption
- 8MB and enormous OS kernel area
The summary of OS of PSP
With GDC, summary was explained concerning OS of PSP. Though as for big topic, the OS kernel was occupying to possess 8MB. The fact that as for the OS kernel of the game machine several hundred KB units quite there is many a thin thing, guarantees the 8MB thing quantity is quite exceptional case. Among the main memories of 32MB of PSP, the user (ゲームデベロッパ) only 24MB it means not to be left.
The fact that kernel possession memory is large many functions is for the controlling PSP. PSP has taken the API based programming model basically, (however, the graphic register list and the like is open) for the sake of, it is presumed that library layer and ratio of the driver are large relatively. Those where amount and the software layer whose extent of abstraction of the hardware is high become thick are reason.
Various OS kernel modules and the low level driver are loaded in the 8MB space, run also the utility applet of PSP. Also the engine such as network, audio and movie playback is included in module. Saving data management and ネットワークコンフィギ…レーション, there is an ounce clean keyboard and various message dialogues etc. in the applet.
In other words, it was not the case that the kernel itself of PSP is the size of 8MB, it is the case that it became the result 8MB, also the space of various engines and protocol stack and the applet etc. guaranteeing. Guaranteeing the space of the applet, in the game, send the game program, is an advantage where it can change to the applet quickly.
The OS kernel guarantees 8MB as the possession area The utility which is loaded in the kernel area
As for the graphic library with 3 classes, as for LibGU OpenGL like (it is not 100% interchangeable) Class of audio library
- The main memory of PSP which originally is 8MB
Those where it is interesting at the OS kernel area of 8MB are the point where the quantity of the main memory of PSP which SCEI at the beginning has planned is 8MB. In other words, when the cover is opened, it is the case that consumes the main memory quantity of originally plan with just the OS kernel of SCEI side. When SCEI has advanced PSP with the specifications of 8MB memory of according to of original plan, the possibility of having become something whose also OS development of SCEI side is very difficult is high.
Concerning the main memory of PSP, you say that the last of the specifications of PSP at stage of the り adjusting which is done, there was a considerable friction. EDRAM (it installed from viewpoint of semiconductor production and DRAM) it was only and from the viewpoint of SCEI and the game development which we would like to hold down to 8MB the memory quantity of PS2 class opinion struck between desired ゲームデベロッパ. Finally SCEI side on ゲームデベロッパ side, listening opinion concerning the desirable memory quantity. Because the opinion of 32MB is many preponderantly, there are the details that it actualized 32MB main memory with the DDR memory of 256Mbit as an external.
Is because it made the transplantation from PS2 of 32MB memory easy and applies that ゲームデベロッパ side desired 32MB. But because the OS kernel possesses 8MB really, like PS2 which almost could use 32MB freely you cannot use memory. Though, with PS2 does not prepare as for the module, because it is there is on a OS side, the memory necessary quantity PS2 compared to decreases on デベロッパ side depending upon the software.
As for case of the memory quantity of PSP showing, the hardware design of SCEI questions, development of software architecture, it sows, being able to link it is to be the possibility without of being. If the software architect has related closely at stage of the hard design, it is presumed that probably there was no complication at the memory quantity. If the abstraction with the software is made thick, the memory quantity to be more becomes necessary.
What you can see the mismatch of the design of this hard and the software the time, is the weak point of SCEI. It has become the big difference with Microsoft where especially software architect side decides the specification of hard. Though, the device development itself which designates, the personally owned semiconductor technology of SCEI as the base is big strength. If it is not that, it is difficult to make the game machine like PSP.
- There is no region cord/code in the UMD game
With GDC concerning the profile and the file format etc. of UMD it was explained. As for UMD, under present conditions there is a profile of 3 types of PSP game and UMD Audio and UMD Video. Concerning the PSP game among these, the region cord/code is not set. But, as for audio and video, it is the possibility that it is restricted.
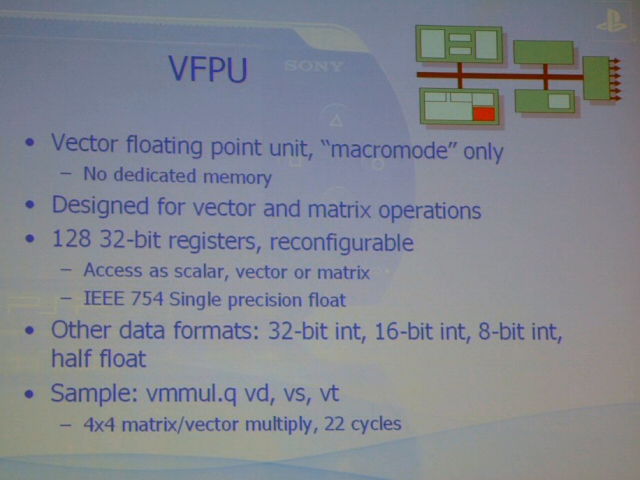
With GDC "VFPU (vectoring floating point arithmetic unit)" of the CPU core of PSP concerning, summary made clear. As for the CPU core of PSP with the R4000 core of MIPS32 instruction set, VFPU has belonged as an extended arithmetic unit. VFPU is designed by for vectoring and matrix operation, supports the 32bit single precision floating point format of IEEE 754. The matrix of 4x4/product-sum operation of vectoring has become 22 サイクルレイテンシ.
VFPU 128 these コンフィギ…ラブル has the 32bit register, also scalar operation has become possible not only vectoring and the matrix. It is seen at the time of vectoring and the matrix that the plural registers are combined. In addition, also the floating point data of 32/16/8bit integer and half size can handle. In other words, PSP being relatively powerful, stacks VFPU whose is widely used.
http://pc.watch.impress.co.jp/docs/2005/0323/kaigai166.htm
Current PSP only efficiency of 2/3 being able to show the reason which is not
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- As for operational frequency it was not 333MHz and was 222MHz
The PSP tip/chip was operational to tell the truth with only the clock of 2/3 of the specifications. Current PSP still being able to show full performance means not to be. In addition, the OS kernel of PSP among the main memories of 32MB, had possessed the 8MB thing area. This is large to exceptional case as a OS kernel area of the game machine.
The motherboard of PSP
In the middle of March was held "GDC (Game Developers Conference)" with, the side which is not excessively known so far generally concerning PSP, made clear. SCEA (Sony Computer Entertainment America), the session which is entitled "PSP Advanced Software Overview" was done with GDC. Among those, Mark DeLoura of SCEA (Manager of Developer Relations), update and software layer of the PSP hardware specifications and the entire image of the tool were explained.
In former official announcement, as for operational frequency of the CPU core of PSP with コンフィギ…ラブル, it was the expectation which operates at most 333MHz. But, with GDC, as for the CPU core of PSP, as for present condition when it is restricted in 222MHz, it was explained. It means to be held down to the clock of 2/3 of the specifications exactly. In addition, also bus speed, 166MHz at the time of specifications announcement of the year before last (reverse operation) from is backing up to maximum 111MHz from zone.
"As for CPU is the range to 333MHz, but under present conditions it is locked to 222MHz. Because the bus is typically the half of CPU (the clock), it has become 111MHz. When CPU is pulled up to 333MHz, when deciding, also the bus is pulled up probably will be to 166MHz, "that DeLoura explains.
The down grade to 222MHz has suggested that in provisional specification, there is a possibility of pulling up in the future to 333MHz. In the future, moving to 65nm process and the production process after the that, perhaps at the stage where electric power consumption goes down, to 333MHz it makes improvement possible.
SCEA did not explain the reason where it is restricted to 222MHz finely. But, as recognized even from the fact that this specification modification is explained with the corner of economical electric power, as for low frequency conversion for electrical retrenchment as for being it is clear. PSP, under the present conditions of 222MHz, to use comfortably with the lithium ion battery of 1,800mAh as an operation and a game machine of 4 - 6 hours, is the last line. Because of that, above this increasing CPU frequency, increasing electric power consumption, it is presumed that it was not possible to shave battery drive time. It seems that as for actual solution with semiconductor technology of present condition, is not 333MHz and is 222MHz.
Summary of CPU core. Frequency has become 222MHz with default The graphic engine under present conditions operates with 111MHz
- The electric power consumption decrease of PSP whose hardship is many
Those where it is distinct from the frequency lock of PSP, are that also SCEI and have suffered hardship in electric power consumption decrease. Especially, in case of PSP becoming problem TDP (Thermal Design Power: It is average electric power consumption not only thermal design electric power consumption). As for average electric power consumption, because leak (a leak) electric current echoes largely, with the process which the present time refines it is very difficult to lower. With improvement such as process technology and circuit design, how much can reduce leak electric power, it is one of the future technical hurdles of PSP.
Though, when you look at the whole PSP, the fact that electric power is eaten on the other hand seems like the device other than main chip set. In the explanation with GDC, seeking and the wireless LAN of UMD drive (Wi-Fi), high brightness setting and the like of liquid crystal display, when it is the operation which consumes electric power very it was explained. Conversely, as for electricity consumption being little, you say that it is the media engine, the bus and the memory stick.
As for the media engine which includes AVC decoding because rather to hard wired it is converted, electricity consumption is little. In 2004 August HotChips conference as for average electric power consumption at the time of AVC decoding below 500mW it was explained. As for the bus, it is seen that is, because economical electrical conversion is possible by the fact that it TURNS OFF briskly.
PSP in the future economical electrical conversion of UMD drive and wireless LAN module etc. becomes necessary. In order with GDC to hold down the access to UMD, it called. In addition, economical electrical conversion of wireless LAN module, as wireless LAN corresponding title increases, probably becomes the important element.
The 222MHz lock is produces effect to also software development. For example, when at the point in time when it reaches the point where it can utilize the frequency to 333MHz, the software where the load which uses the full CPU clock is high was made, there is a possibility the case where compatibility of the current type of 222MHz becomes problem coming out. But, when you see in positive, PSP specifications means to be the margin where still it improves performance.
The largest obstacle economical electric power of PSP. As for CPU under present conditions lock to 222MHz When developing the battery emulator tool in order to optimize electric power consumption
- 8MB and enormous OS kernel area
The summary of OS of PSP
With GDC, summary was explained concerning OS of PSP. Though as for big topic, the OS kernel was occupying to possess 8MB. The fact that as for the OS kernel of the game machine several hundred KB units quite there is many a thin thing, guarantees the 8MB thing quantity is quite exceptional case. Among the main memories of 32MB of PSP, the user (ゲームデベロッパ) only 24MB it means not to be left.
The fact that kernel possession memory is large many functions is for the controlling PSP. PSP has taken the API based programming model basically, (however, the graphic register list and the like is open) for the sake of, it is presumed that library layer and ratio of the driver are large relatively. Those where amount and the software layer whose extent of abstraction of the hardware is high become thick are reason.
Various OS kernel modules and the low level driver are loaded in the 8MB space, run also the utility applet of PSP. Also the engine such as network, audio and movie playback is included in module. Saving data management and ネットワークコンフィギ…レーション, there is an ounce clean keyboard and various message dialogues etc. in the applet.
In other words, it was not the case that the kernel itself of PSP is the size of 8MB, it is the case that it became the result 8MB, also the space of various engines and protocol stack and the applet etc. guaranteeing. Guaranteeing the space of the applet, in the game, send the game program, is an advantage where it can change to the applet quickly.
The OS kernel guarantees 8MB as the possession area The utility which is loaded in the kernel area
As for the graphic library with 3 classes, as for LibGU OpenGL like (it is not 100% interchangeable) Class of audio library
- The main memory of PSP which originally is 8MB
Those where it is interesting at the OS kernel area of 8MB are the point where the quantity of the main memory of PSP which SCEI at the beginning has planned is 8MB. In other words, when the cover is opened, it is the case that consumes the main memory quantity of originally plan with just the OS kernel of SCEI side. When SCEI has advanced PSP with the specifications of 8MB memory of according to of original plan, the possibility of having become something whose also OS development of SCEI side is very difficult is high.
Concerning the main memory of PSP, you say that the last of the specifications of PSP at stage of the り adjusting which is done, there was a considerable friction. EDRAM (it installed from viewpoint of semiconductor production and DRAM) it was only and from the viewpoint of SCEI and the game development which we would like to hold down to 8MB the memory quantity of PS2 class opinion struck between desired ゲームデベロッパ. Finally SCEI side on ゲームデベロッパ side, listening opinion concerning the desirable memory quantity. Because the opinion of 32MB is many preponderantly, there are the details that it actualized 32MB main memory with the DDR memory of 256Mbit as an external.
Is because it made the transplantation from PS2 of 32MB memory easy and applies that ゲームデベロッパ side desired 32MB. But because the OS kernel possesses 8MB really, like PS2 which almost could use 32MB freely you cannot use memory. Though, with PS2 does not prepare as for the module, because it is there is on a OS side, the memory necessary quantity PS2 compared to decreases on デベロッパ side depending upon the software.
As for case of the memory quantity of PSP showing, the hardware design of SCEI questions, development of software architecture, it sows, being able to link it is to be the possibility without of being. If the software architect has related closely at stage of the hard design, it is presumed that probably there was no complication at the memory quantity. If the abstraction with the software is made thick, the memory quantity to be more becomes necessary.
What you can see the mismatch of the design of this hard and the software the time, is the weak point of SCEI. It has become the big difference with Microsoft where especially software architect side decides the specification of hard. Though, the device development itself which designates, the personally owned semiconductor technology of SCEI as the base is big strength. If it is not that, it is difficult to make the game machine like PSP.
- There is no region cord/code in the UMD game
With GDC concerning the profile and the file format etc. of UMD it was explained. As for UMD, under present conditions there is a profile of 3 types of PSP game and UMD Audio and UMD Video. Concerning the PSP game among these, the region cord/code is not set. But, as for audio and video, it is the possibility that it is restricted.
With GDC "VFPU (vectoring floating point arithmetic unit)" of the CPU core of PSP concerning, summary made clear. As for the CPU core of PSP with the R4000 core of MIPS32 instruction set, VFPU has belonged as an extended arithmetic unit. VFPU is designed by for vectoring and matrix operation, supports the 32bit single precision floating point format of IEEE 754. The matrix of 4x4/product-sum operation of vectoring has become 22 サイクルレイテンシ.
VFPU 128 these コンフィギ…ラブル has the 32bit register, also scalar operation has become possible not only vectoring and the matrix. It is seen at the time of vectoring and the matrix that the plural registers are combined. In addition, also the floating point data of 32/16/8bit integer and half size can handle. In other words, PSP being relatively powerful, stacks VFPU whose is widely used.
http://pc.watch.impress.co.jp/docs/2005/0323/kaigai166.htm